How to Upload Disavow File Google Search Console
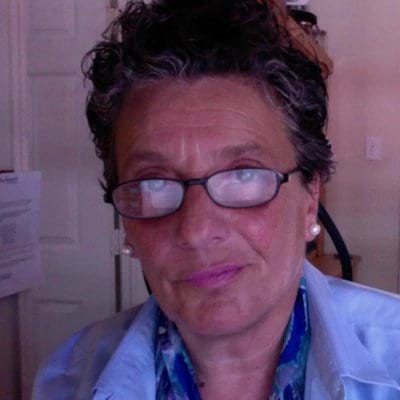
Skilful backlinks help a site rank higher. Bad backlinks tin cause issues. Yous have only limited control over which links betoken to your site. If y'all've spent any time in SEO, these are things y'all already know. You also know that Google'south "Disavow Links Tool" can help protect your site from link-related penalties. Even with that knowledge, most SEOs—even leading experts—answer the question, "Should I disavow?" with an emphatic, "It depends." And SEO "best practices" (e.one thousand., "Disavow only bad links that are harming your site") assume that it'due south easy to carve up links that boost rankings from those that threaten them. In this commodity, I'll explain when you should (and shouldn't) disavow links, and how to identify "bad" links. But first, you should sympathize why Google created the disavow tool and how its use has changed over the years. Google's Disavow Links Tool lets you tell Google to ignore specific backlinks for ranking purposes. Similar a rel="canonical" tag, a disavow file is a "strong suggestion rather than a directive." The technical procedure is uncomplicated: You submit a text file containing the linking pages or domains that you lot want to disavow via Google Search Console (GSC). (More on this later.) The decision-making process—determining which domains should be in the disavow file or whether yous should disavow at all—is more complicated. To brand that determination, you need to understand: Google has fought spammy link-building for more than a decade. Its outset effort to reduce link spam was the introduction of the "nofollow" attribute in January 2005, which sought to combat comment spam like this: While Google continued to conform its algorithm in subsequent years, the next significant change targeting link schemes didn't occur until April 2012, when Google rolled out the kickoff Penguin algorithm. Penguin was an "external filter" through which search results passed. That technical particular meant that an algorithmic penalisation could persist for months afterwards a thorough site clean-upwardly. Google supplemented algorithmic penalties with Transmission Deportment, which it sent to webmasters if it "detected a blueprint of unnatural artificial, deceptive, or manipulative outbound links." An unabridged site could be demoted even when a link scheme targeted a subsection or unmarried page of a website. The Disavow Links Tool, then, gave webmasters more control over the links that Google used to rank—or potentially penalize—their site. Even at its rollout in October 2012, Google believed the disavow tool practical to a limited number of webmasters: If you've been notified of a manual spam action based on 'unnatural links' pointing to your site, this tool can help you lot accost the consequence. If you haven't gotten this notification, this tool generally isn't something you demand to worry almost. The tool wasn't intended so (or now) equally a first line of defence against link-based penalties. As Matt Cutts explained in a 2012 interview, it could expedite site recovery after manual methods were exhausted: Right now it can be a difficult job to clean upwards a site's backlinks, and from listening to the SEO customs we wanted to provide a tool that could help after site owners had already taken substantial steps to try to clean up their site'south backlinks. Through the showtime iii iterations of Penguin, most SEOs believed that disavowing links was essential to protect sites from lengthy demotions in search results. Consensus changed with the introduction of Penguin 4.0, which Google released in September 2016. Penguin iv.0 marked Google's update to a "real-time" Penguin algorithm, which also allowed Google to target link spam at a page-specific level. Most importantly, it marked a fundamental shift from "demoting" to "devaluing"—from algorithmic wrath to algorithmic apathy: Then began the great debate: Is disavowing all the same necessary? And if so, when? What constitutes a "low-quality" link? What is a "bad" directory? What is a "good" guest post? Co-ordinate to Google, a depression-quality link is one that is: […] intended to dispense PageRank or a site's ranking in Google [or] may be considered part of a link scheme and a violation of Google'south Webmaster Guidelines. This includes any beliefs that manipulates links to your site or outgoing links from your site. Gabriella Sannino, the founder of Level343, simplifies that definition for her link audits: A skilful dominion of thumb is, if the link isn't relevant to your site or your users, it probably shouldn't be in your contour. Marie Haynes applies a similar logic: Does the link serve any purpose outside of SEO? Does this link have legitimate potential to bring business to my site? In contrast, Google notes that loftier-quality links are often "editorially earned": Links are usually editorial votes given by option, and the more than useful content you have, the greater the chances someone else will discover that content valuable to their readers and link to it. At that place's plenty of space for subjective interpretation betwixt these definitions: Still, there are some unambiguously "bad" links, and taking the time to investigate their origin and timing tin can help identify if a customer is unknowingly paying another agency to build them. (This can assist y'all stop the leak instead of just bailing h2o.) Here are six clear-cutting sources of bad links: Google targets a subset of paid links: not-editorial, dofollow links that are clearly designed to pass PageRank. While some paid links may exist difficult to detect, there are a few ruby-red flags: Google began actively de-indexing PBNs in 2014. They still exist, but links from PBNs are not part of any white-hat link-building strategy. PBNs are a focus of link audits past Ryan Stewart and his team at WEBRIS, who […] generally focus on links that were built by humans. The internet is full of garbage and sites tend to pick upwards random links that look spammy but are really just ignored by the algorithm. The only links we disavow are ones from PBNs and low-quality domains with verbal-friction match anchors. To identify a depression-quality directory, enquire yourself: Do you expect to get referral traffic from the listing? If the answer is "No," information technology'south probably low quality. While low-quality directory submissions haven't worked for years (and many now utilize nofollow links that eliminate the need to disavow), some unethical SEOs claim the contrary when pitching their "services" to unsuspecting website owners. A handful of high-quality or niche-specific directories might be worth the fee, simply this tactic is not an effective way to grow site authority. Commenting on relevant, authoritative sites and forums and linking dorsum to related content on your site is not just allowed but encouraged by Google. The trouble is the scaling or automation of that procedure. Many annotate systems now make all links nofollow by default, so there'southward likely piffling risk or reward hither. There's no gray area when information technology comes to hacked websites. Links from hacked sites will all but guarantee a penalisation from Google, and participating in the hacking can also get yous in existent problem. (It's, yous know, illegal.) The most mutual blazon of negative SEO is backlink spamming—intentionally linking back to a competitor from hundreds or thousands of low-quality websites. If you've always logged into Site Explorer and seen a massive, unwarranted jump in referring domains, information technology could bespeak that your site has been attacked: Receiving thousands of spammy links in a short period volition arouse Google'due south suspicion, potentially resulting in a penalisation. Even with a firm grasp of which links are "bad" and which are "expert," disavowing remains risky. A link that looks "bad" may even so assist your site. Google has continued to caution users about the apply of the disavow tool: Despite this warning, the fearfulness of a penalty has led many SEOs to prune links aggressively. Years ago, this overzealous approach was aided by a misinterpretation of advice from Cutts almost the employ of the disavow tool: While the takeaway should take been an endorsement of domain-level rather than URL-level disavowal (read past the highlighted portion above), the indelible audio bite for many was to "disavow with a machete, not a scalpel." Cutts is also on record noting that an effort to "reavow" links takes more time and may weaken the signals sent past those links: [If you want to 'reavow' a link, then that will] take a lot longer, and we might not even requite it the same weight, if we start to allow information technology to exist reavowed. With and so much at pale, but a handful of situations weight the risk-reward adding heavily toward advantage. A Manual Activeness is the one accented "yeah" when it comes to the utilize of the disavow tool: If you have a transmission action, you lot demand to clean upward or disavow the links. For algorithmic things, upward to you. — John ☆.o(≧▽≦)o.☆ (@JohnMu) Oct 25, 2017 Across that, there are two instances when disavowing links is probably (merely not definitely) the right choice: Nonetheless, experts remain divided in these and other situations that tin can autumn into a "gray area." A sample of post–Penguin 4.0 tweets reveals a range of perspectives: Dwindling need for the disavow tool. However in that location if you lot need it, simply Google is treatment spammy links now. https://t.co/mFDY7EbWjd — Glenn Gabe (@glenngabe) March 15, 2018 My Experience: — Cyrus (@CyrusShepard) September 12, 2017 Do Nosotros Still Need Disavow after Penguin four.0? https://t.co/hhGAQYHLSh Penguin isn't GONE, people. It's role of the core algo now. Utilize Disavow — Ian Lurie (@portentint) April 6, 2017 And the disavow IS NOT dead https://t.co/ovJ7tOxokE — Rand Fishkin (@randfish) March 16, 2017 Removing Disavow File… five Months On = 37.31% Increment in Organic Traffic https://t.co/RmEpoFC04D past @kevgibbo — Paul Shapiro (@fighto) March 9, 2017 Google Penguin doesn't penalize for bad links – or does it? — You technically no longer need to use the disavow… https://t.co/YhCcAs7ZNa — duane forrester (@DuaneForrester) September 28, 2016 When we asked a few other well-known SEOs near if they still disavow, the answer was often "Yes, but…": Ryan Bartlett, founder of SEO Direct: Yes, we notwithstanding use it if their link contour appears to be very spammy. Although, it doesn't seem to have as much of an impact every bit it used to Marie Haynes, founder of Marie Haynes Consulting: I do use the disavow tool today, but non nearly equally much as I did prior to Penguin 4.0. In the past I would accept entire days dedicated to link auditing, but that rarely happens now. Google is divided, likewise. Shortly after Penguin 4.0'south release, John Mueller confirmed that the update had no event on disavow recommendations: Aye, nothing changed with the disavow. — John ☆.o(≧▽≦)o.☆ (@JohnMu) October four, 2016 He also noted that it remains valuable if you're seeking peace of mind: The disavow file is a keen way to just similar preemptively say well I know most these bug, I don't want to lose any slumber over them, I'k just going to disavow them and go them taken out of the equation. Nevertheless, while not contradicting Mueller's advice, Gary Illyes was more than dismissive of the need to disavow: "If you practice not accept a manual activity then you practice non need to submit a disavow!" @methode #Pubcon Bang-up questions by @jimboykin — Brian McDowell (@brian_mcdowell) Nov 8, 2017 Illyes also confessed that he'south never submitted a disavow file for his site—or even evaluated his backlink profile: I run my own site, which gets about, perhaps 100,000 visits per week. Information technology's been upward for 4 years perchance and I don't have a disavow file, I don't fifty-fifty know who links to me. And then how practice you brand the right choice with so much "gray expanse"? Information technology requires a holistic evaluation of the customer, the site, and your job. Because disavowing bad links volition have no impact on many sites, you lot must offset make a persuasive example to a client most why it's valuable. Y'all must likewiseposition your disavow effort within a bureaucracy of SEO opportunities. Disavowing links is commonly a secondary priority that protects gains fabricated through other, more valuable SEO tasks. That said: What would the consequences be if the site were penalized? Know that a penalty is a uniquely unforgivable sin for an SEO. It's one of the few specific events for which an agency may lose their client or an annotator their task. (This is what keeps me upwards at night—not an irrational belief in the likelihood of a penalty but the very rational fright of its consequences.) Ultimately, performing a link audit is the just way to know whether or non there is any real need to disavow. Hither's how to do information technology. IMPORTANT! Remember, Google's kickoff recommendation is to remove low-quality links from the web. While this rarely works, you may still demand to effort if y'all're filing a reconsideration request. If you know what a bad link looks like, the rest of the process is but applying that knowledge across a site'southward entire backlink profile. Regular, high-level link monitoring can help determine whether a deep swoop is necessary. Three reports in Site Explorer make that process pretty efficient: the "Referring domains" graph, the "Anchors deject," and the "CTLDs distribution" map. The best part of these reports is that they provide a relative rather than accented assessment—monitoring takes the same amount of time regardless of the size of the backlink profile. Referring domains graph: The referring domains graph can identify a fasten in links, which is often acquired past link spam (self-directed or part of a negative SEO attack). For the optimists out there, information technology may also reveal when a slice of linkbait went "viral." In whatever instance, high "link velocity" is cause for further investigation. Anchors cloud: The anchors cloud can help identify whether links seem suspiciously "over-optimized." In this example from Blanchard'southward Coffee Roasting Co., every ballast in the cloud is a brand term: Brand-heavy anchor text is a safe bet that the link profile is natural and won't enhance any red flags. Compare that to the anchor cloud of a hacked site for a family-run lamp shop in Sweden: If but a single term or two raises suspicion, y'all can choose the "Anchors" report and "Details" to see the referring domains and backlinks with the apropos ballast text: CTLDs distribution map: The land lawmaking tiptop-level domain (CTLD) map is likewise a quick fashion to evaluate a backlink profile. This example is troubling. The website is for a SaaS provider with an exclusively U.S. customer base, yet its most common CTLDs are from Colombia, Libya, and Russia: If everything looks practiced across these three reports, y'all can probably move on to something else. However, if you're growing increasingly suspicious, information technology's time for a full link audit. The quality of a link audit depends heavily on the comprehensiveness of the source materials. For the fullest possible moving picture, consider pulling Google Search Console data into your backlink analysis. In nigh cases, all the same, the link profile in Ahrefs can serve as a stand-solitary source. Go to Site Explorer -> Enter your domain -> Backlink Contour -> Referring Domains -> Filter for dofollow links -> Sort by DR (low to high) Quick tip Do you prefer working in a spreadsheet? Striking "Consign" to download the data in Excel format. 🙂 Two markers are good places to showtime link evaluation: Neither is a guarantee that a link is bad, merely together the metrics offering a useful way to sort links. You should already have sorted by DR (low to high), merely you can as well employ the congenital-in filters to filter for specific TLDs. E.g., .ru, .cn, etc. This example from a fitness blog has it all: depression DR, a spammy domain name and page title, and spammy anchor text. Disavow such spammy links at the root-domain level. If an offending link comes from a trusted domain, disavow information technology at the URL level. As Illyes has emphatically noted, exercise not disavow major domains because of a single strange link: I was looking at people who disavowed links from CNN and from the telegraph and whatever considering they just didn't know why would, or why did they get that link. That was bat shit stupid. You tin can flag domains for disavow in your spreadsheet or directly in Ahrefs. Check the boxes and click "Disavow Domains" next to any domains you desire to add together to your list: The next fourth dimension y'all consign your disavow file from Ahrefs, it will include these domains. If you desire to reavow the domains, the process is simple (if simply it were this like shooting fish in a barrel in Google): If a domain falls into a gray expanse, flag it in a spreadsheet as "questionable." Afterward plowing through a full backlink contour, it's easier to spot patterns among "questionable" links to aid decide whether to disavow them. In one case you've identified all the domains yous want to disavow, just format your listing for the disavow file and upload it in GSC. Google details the stride-by-step procedure for disavowing links in GSC, including how to format the text file. Earlier you create a new disavow file, download the most recent one from GSC. A disavow list is cumulative, and a previous webmaster or agency may have already submitted a disavow file. (If you didn't create the existing disavow file, review it before adding to it. A prior attempt may take disavowed valuable links.) Formatting a new disavow file is straightforward, and GSC volition alert you of any errors upon submission. Most errors result from a failure to strip the protocol or subdomain prefix from the root domain. If you've disavowed links within Ahrefs, you lot tin employ Ahrefs to format your disavow file for you. On the chief Dashboard screen, click "Disavow links" in the row with the desired website, then choose "Export." Check the "Save as TXT for upload to Google Disavow Tool" box and click "Ok": Y'all can add together comments to annotate each update of your disavow file: Just don't waste your time with any explanations or pleading to the non-sentient machine that volition process it. These comments are for you—not Google. Also, don't worry that submitting a disavow file will make Google more probable to investigate your site's links. (It won't.) Information technology may take weeks for the effects of a disavow endeavor to become visible. Google needs to recrawl the disavowed links to adjust its evaluation of your site'due south backlink profile. Annotate the disavow file upload in Google Analytics (or another analytics platform) and monitor the site advisedly. Yous can also upload the submitted disavow file back to Ahrefs: This will give you lot cleaner link information in Ahrefs and expedite the disavowal process in the future. The Disavow Links Tool has given webmasters more control over how Google evaluates the links pointing to their site. That control was vital in the pre-Penguin 4.0 era. Penguin 4.0 has changed some annotator perspectives, simply monitoring and assessing a backlink profile remains a core part of SEO—regardless of whether y'all disavow. At present it'due south your turn: How are yous reshaping your approach to link monitoring and disavowal in 2018? Share your expertise past joining the conversation below.What is Google'south "Disavow Links Tool" and why did they create information technology?
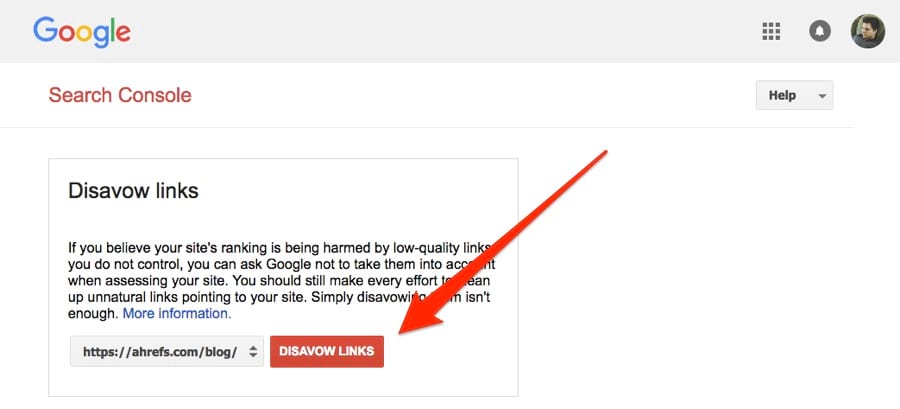
Why did Google create the Disavow Links Tool?
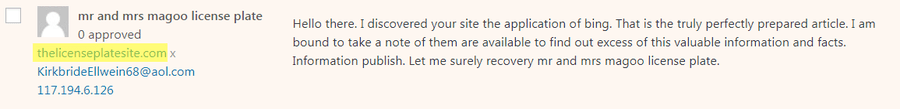


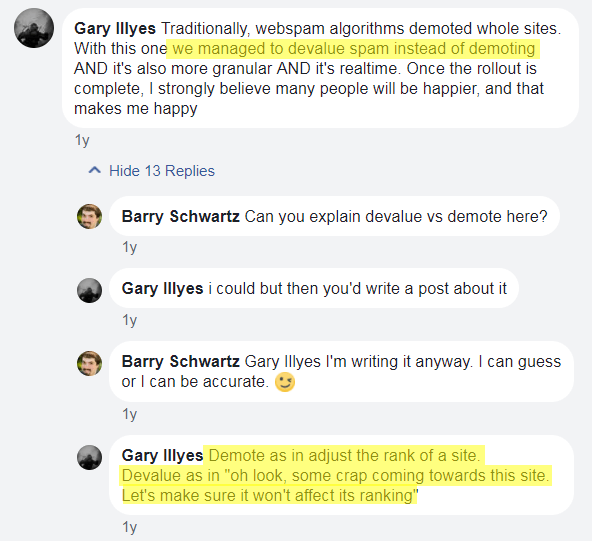
When should (or shouldn't) yous disavow?


i. Paid links
2. Private Blogging Networks (PBNs)

iii. Depression-quality directories
iv. Comment and forum spam
five. Hacked sites
6. Negative SEO
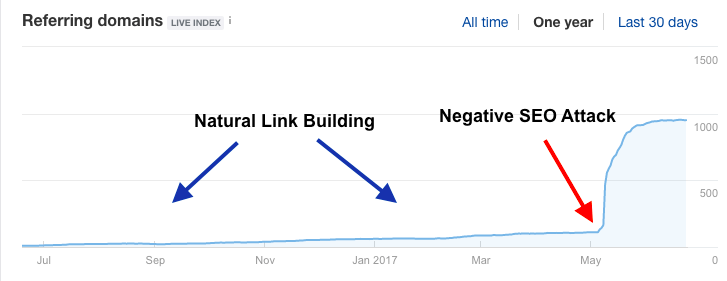
What are the risks of disavowing?



And then when should you disavow?
1) Google'southward Disavow Tool works
2) It tin can also practice damage
three) Poll says 62% of SEOs use it, 38% don't https://t.co/hryP62JzvA picture.twitter.com/mpJ6BY353e


How to identify and disavow bad links
Pace 1. Perform a loftier-level link audit
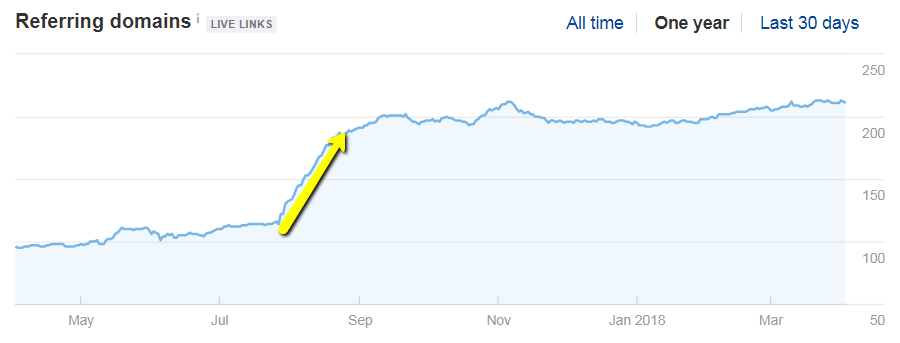


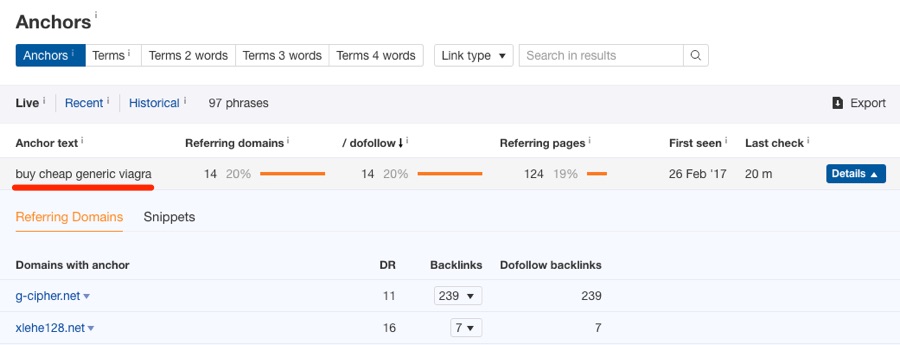
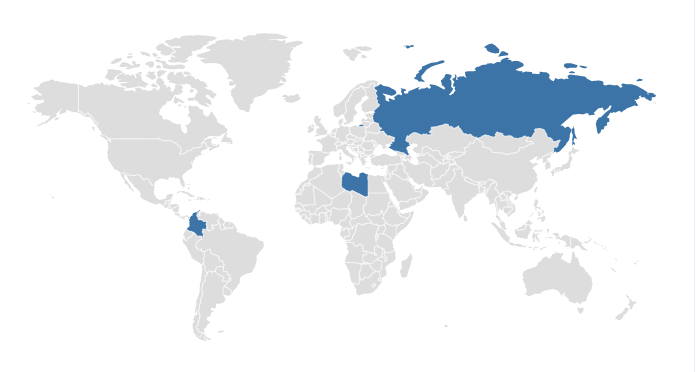
Step 2: Perform a full link audit (if necessary)
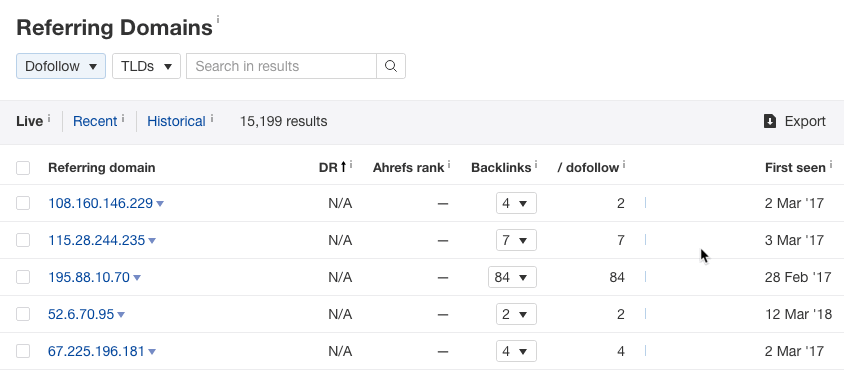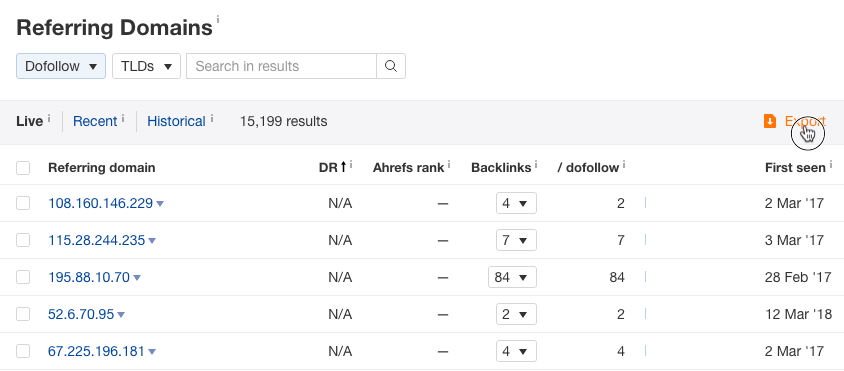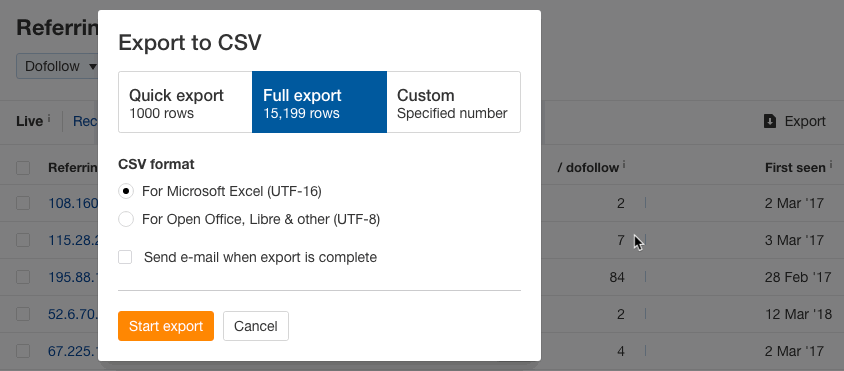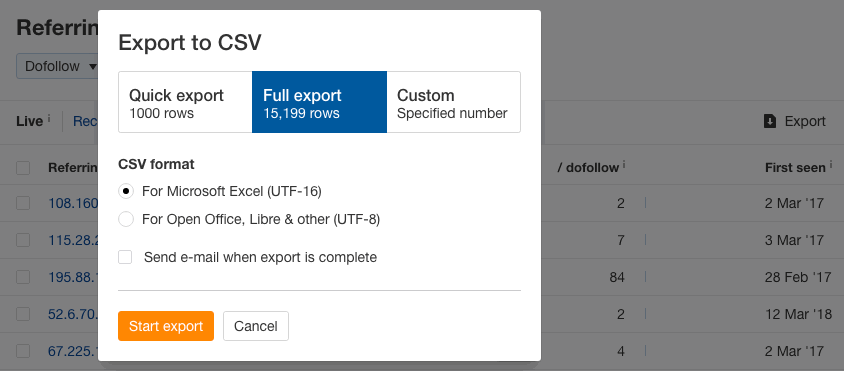
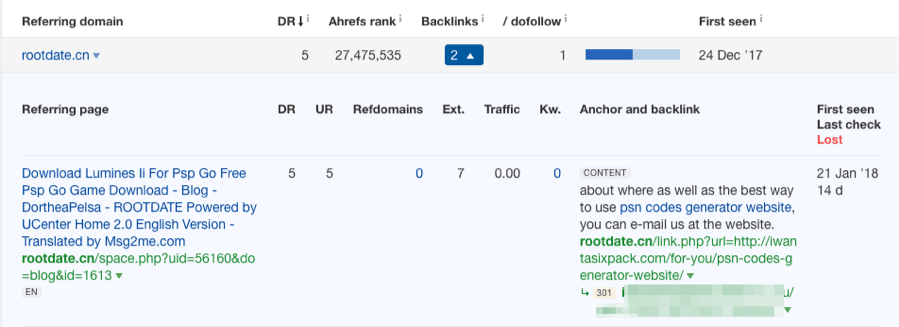
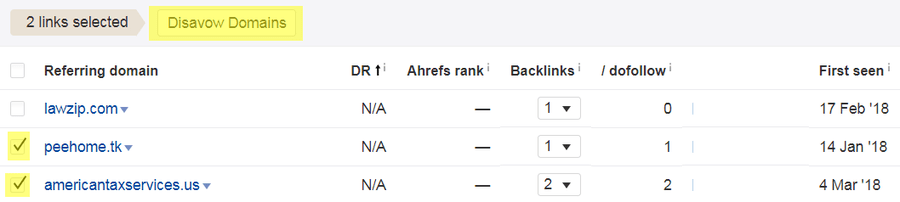
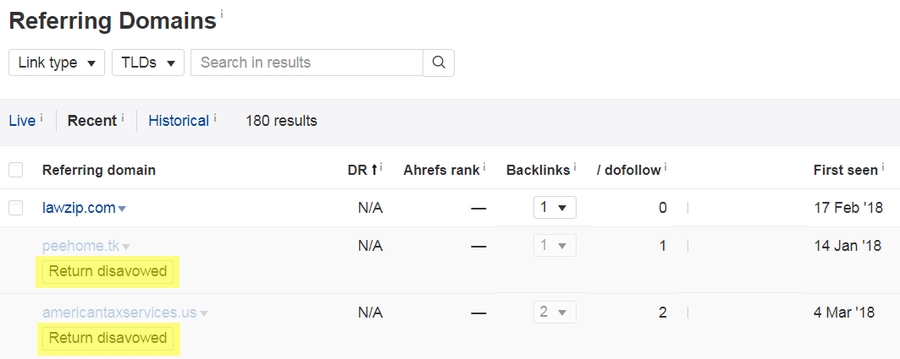
Step 3. Format and upload your list to Google'south Disavow Links Tool
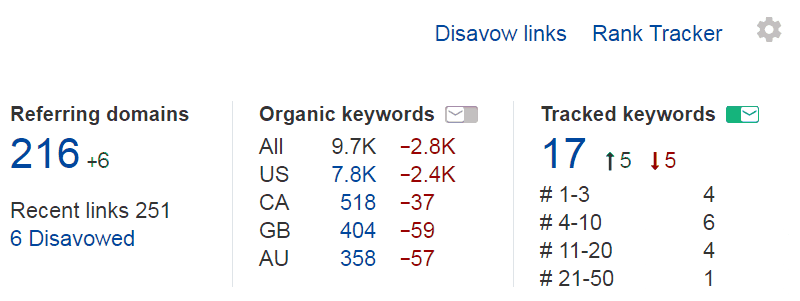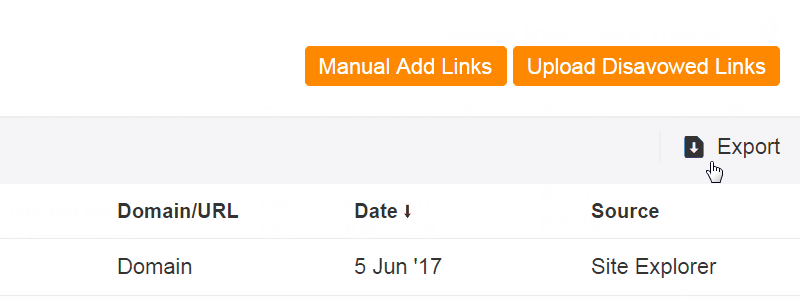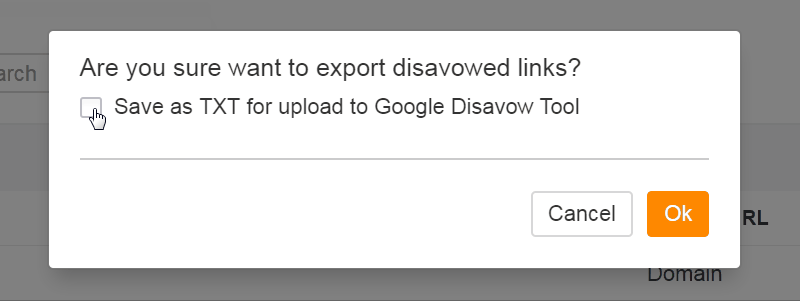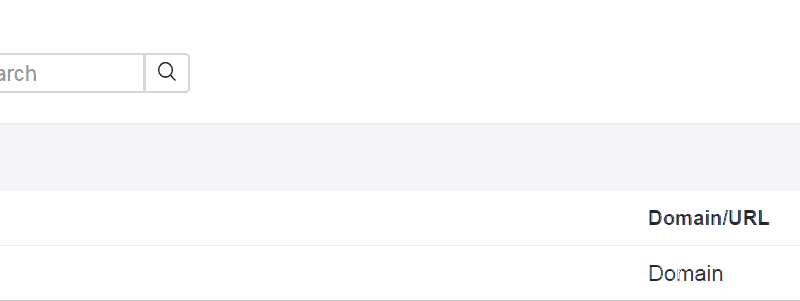

Step 4. Log your changes and monitor progress
Final thoughts
Source: https://ahrefs.com/blog/google-disavow-links/
0 Response to "How to Upload Disavow File Google Search Console"
Post a Comment