What Brain Changes Are Consistent With Premature Babies
Abstract
It is extremely mutual for babies to be born early on. When babies are born likewise early, their normal brain development is interrupted, and they are more than likely to have problems later on in their lives. Disrupting brain development results in various types of brain injury depending on how early the baby is born. Even babies who are born a footling bit early on can accept brain injury. It is important to understand the differences in brain development betwixt babies who are built-in at full term compared with those who are born early. Knowledge of these differences allows scientists and doctors to find new treatments for babies who are born early on. It is very of import to minimize brain injury, and so that these babies get off to a good start.
Introduction
It is really exciting when a family unit is making plans for a new baby. Equally the anticipation builds, information technology might seem like the sooner the infant arrives the improve. However, babies demand to complete important stages of brain development earlier they are built-in. Doctors consider babies born before they accept reached the normal 37–40 weeks of fourth dimension inside the mother to be "preterm" (Figure 1A). Worldwide, almost 11% of babies are built-in preterm [1]. Nearly of these babies are born simply a few weeks early. A small group of these babies are born extremely preterm, meaning they are born before 28 weeks of development. The earlier a infant is born the more vulnerable their brain is to injury. Brain injury can happen when a baby is born early on because the babe's brain development is disrupted. The encephalon injuries that babies experience can affect them for the rest of their lives. Doctors and neuroscientists are still trying to sympathise how to help the brains of preterm babies develop normally and reduce brain injury so that the babies practice not have bug with their brains when they grow upwards.
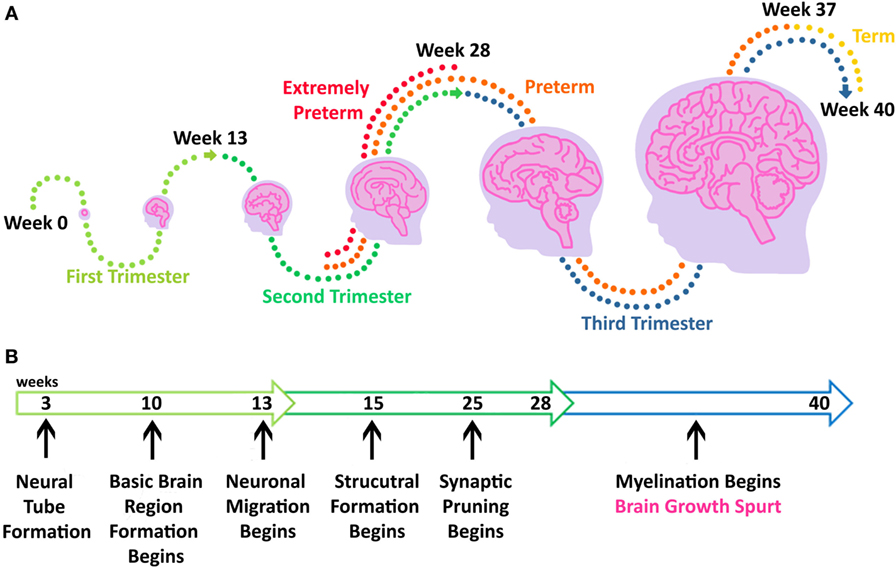
- Figure ane - This figure shows the stages of pregnancy too every bit the events in man brain development.
- A. A timeline of the three trimesters of pregnancy. Babies who are born early, before 37 weeks, are called preterm (orange dots). Preterm babies who are born between week 22 and week 28 are chosen extremely preterm (red dots). Babies are born on time if they are born "at term," between week 37 and week twoscore (yellow dots). B. Brain development is a series of circuitous steps. Black arrows point to specific events in brain evolution that happen on sure weeks throughout a pregnancy. One of the beginning steps in brain evolution happens at calendar week three, when the neural tube forms. Myelination is one of the terminal steps of encephalon development that happens during the third trimester of pregnancy, when the brain undergoes a massive growth spurt.
Brain Development
Pregnancy is divided into three split up stages called trimesters . Very specific developmental events occur in each trimester (Figure 1B). Understanding how a baby's brain develops during each phase is the starting time stride in determining what kind of brain injury a preterm infant might have.
Brain evolution begins during the starting time trimester with the formation of something called the "neural tube." The neural tube is a group of cells that will eventually grade the entire brain and spinal cord. The neural tube cells separate over and again, to form the bones regions of the brain. It is crucial to understand that only the basic construction of these brain regions is established during this early on time, and that it is only later in development, fifty-fifty into adolescence in some cases, that these regions cease growing. Around 8 weeks into the first trimester, a massive movement of neurons begins. These neurons are considered the thinking cells of the brain. They originate from specific areas of the brain where new cells are formed and travel through the brain tissue to their last destinations. This motion of newly formed neurons, called "neuronal migration," continues for the balance of brain development.
Of import stages in encephalon evolution also occur in the second trimester of pregnancy. Early in the second trimester, more advanced brain structures begin to course out of the full general structures that were established during the first trimester. These structures form as more and more than neurons migrate into the regions. When a neuron arrives at its destination, information technology makes connections with other neurons. These connections are called synapses , which is where one neuron passes a message to another neuron. In the middle of the 2d trimester, the of import process of "synaptic pruning" begins. At this phase of brain development, neurons have made synaptic connections with as many other neurons as possible. But as development continues and as neurons start to send messages to one another, not all of the connections are necessary. Synaptic pruning is the procedure of removing the extra connections that are not being used. This removal makes the brain regions more than organized, so that only the essential synapses remain. The process of synaptic pruning continues later a infant is born.
DID YOU KNOW? Neurons in the brain are i of the most unique prison cell types in the human body. Neurons are able to talk to each other using electricity and chemicals called "neurotransmitters". Neurons use electricity to carry a message to a different part of the brain where the message is then translated into a chemic packet that is sent to other neurons!
During the third trimester of pregnancy, a brain growth spurt occurs. From the starting time of the third trimester to the end of the third trimester, the baby's brain will almost double in size [2]. The brain grows then quickly for two reasons. The start is that processes that started earlier in development are ongoing, such as the forming and migration of new neurons and other types of brain cells. The 2d reason for this rapid growth is that the procedure of "myelination" begins. Myelination is when a certain type of brain cell, called an "oligodendrocyte," wraps the axons of neurons with a substance called myelin (Figure two). The axon is a skinny arm on the neuron that reaches to other parts of the encephalon. The myelin wrapping allows messages to travel downwards the length of the axon and so that neurons can communicate with each other much more rapidly than earlier the myelin was there. Myelin also provides the axon with materials information technology needs to stay good for you.
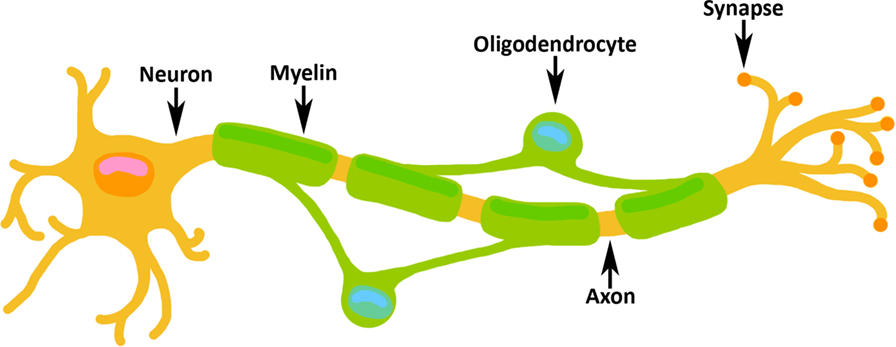
- Figure ii - Oligodendrocytes brand myelin, which wraps the axons of neurons during the third trimester of pregnancy.
- Myelin allows a message to exist sent down the axon to the synapse, where the message is then passed on to another neuron. The neuron receiving the message, called the postsynaptic neuron, is not shown.
When term babies are born, between 37 to 40 weeks, their brains have completed these complex stages of development and their brains are ready to see the world. If babies are born early, their brain development is interrupted.
Interrupted Encephalon Development
Doctors who have care of preterm babies are worried about these babies developing brain injury. Ane fashion that brain injury can occur in babies born early on is past interrupting brain development, causing their brains to develop in a way that is dissimilar from that of babies born at term. The amount of brain injury depends on how early a baby is born and on how healthy the baby is. Overall, babies who are born only a little early accept a amend chance of avoiding brain injury. Extremely preterm babies have not completed as many steps in encephalon development and thus have more bug with brain injury. Depending on how early on a baby is built-in and which steps in brain development were interrupted, doctors and scientists can make predictions near the kind of brain injuries the preterm babies could have and how these encephalon injuries could affect these babies when they grow up.
Extremely preterm babies are born during the 2d trimester when the structures and regions of their brains are nonetheless in the procedure of forming. On the outside of the encephalon, a bumpy texture made up of grooves and ridges is formed during this fourth dimension. The grooves are called sulci and the ridges are called gyri. When the germination of the sulci and gyri is interrupted, and they practice not develop normally, these babies are at risk of developing a condition chosen epilepsy equally they get older, which is when seizures occur multiple times. There are also regions on the inside of the brain that undergo of import developmental milestones during the second trimester. The corpus callosum is i of these regions. The corpus callosum is a group of axons wrapped in myelin that carries messages from neurons on ane side of the brain to neurons on the other side of the brain. In extremely preterm babies, the germination of the corpus callosum is interrupted and the axons crossing the span from ane side of the brain to the other side are disorganized and are not able to send messages besides [3].
DID YOU KNOW? In a normal man brain, there are more 200 million axons that cross the corpus callosum to send messages from one side of the brain to the other. Recently, scientists examining the brain of the famous physicist, Albert Einstein, discovered that his corpus callosum was much larger than normal [four]! Could this mean that more connectivity between the 2 sides of the brain contributed to how smart Einstein was?
Even when a infant is built-in simply a niggling bit early, there is nonetheless a take chances that the baby could have brain injury from aberrant encephalon development. During the third trimester, the process of myelination starts. If this process is interrupted, the myelin that supports axons might not develop unremarkably. When these babies grow upwards, they could have trouble focusing in schoolhouse and difficulty in learning certain subjects.
Brain injury in preterm babies not only comes from interrupting brain evolution before the babies are born just also happens later on birth. Preterm babies are at hazard of encephalon injury resulting from sudden changes in their surroundings. For instance, being inside the female parent is a very different environment compared with beingness in the neonatal intensive care unit (the place in a hospital where doctors take care of ill babies).
Sensory Overload
When a preterm baby is born, the environment that the baby's brain is developing in is very unlike from what information technology is supposed to be. The change in environs can crusade brain injury because the developing encephalon must now procedure all the information from the new environment before information technology is fix to do so. To make things even more than complicated, babies who are born early tin can be really sick in other ways, which can likewise impact encephalon evolution.
Preterm babies experience brain evolution in a very different environment (a hospital room) compared with babies who are born at full-term, whose brains develop inside of the mother (Effigy 3). Scientists think that when the brain of a preterm baby develops outside of the female parent, information technology receives inappropriate signals from the surroundings that bear on how the neurons are organized. The preterm baby'southward brain is forced to process information coming in from the ears (sounds), eyes (light), nose (smells), oral cavity (tastes) and skin (touch) before the infant is set to receive that sensory information. Scientists think that this kind of sensory overload might lead to the abnormal brain connections and encephalon structure in kids who were born extremely preterm [five]. Because we have learned that this early sensory overload might contribute to brain injury and aberrant evolution in preterm babies, doctors now recommend certain techniques to control the environment that these babies develop in, and then that their encephalon injuries are non fabricated worse. Almost of these techniques try to mimic what the touches, sounds and lights would be similar if the baby had not been built-in early.
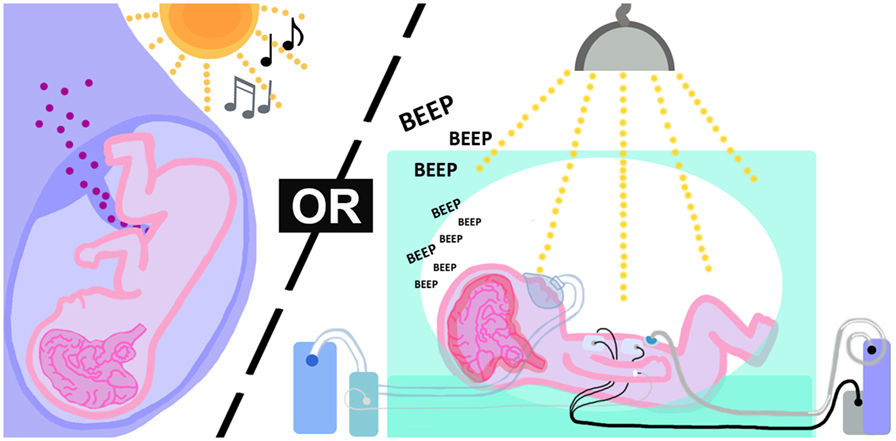
- Figure 3 - This figure shows some of the differences in the environment that preterm babies live in while they go through brain development, compared with babies who have not been built-in yet.
- A preterm baby experiences different kinds of sensory input from the environment (sounds, lights and affect) that can hurt the baby'due south encephalon.
When a infant is born early, the baby leaves the mother'due south body and enters the world before they are ready. Non merely is the babe's encephalon non fix to procedure information but also the infant's body is not prepared to handle all of the challenges that come up with living outside of the female parent. Preterm babies are likely to become sick, which can cause further brain injury. Even though both term and preterm babies can go sick after being built-in, preterm babies are at a disadvantage, considering their torso systems and organs are at an earlier stage of development.
Outside of the mother, a baby can go sick from bacterial, viral or fungal infections. Inflammation is a normal and important process carried out by the trunk's immune system that helps fight off infection. However, when a preterm baby is ill with an infection, the inflammatory response can actually harm the baby's developing brain. Other challenges that preterm babies face up include problems with claret period to the brain and diet for the brain cells. Claret period delivers oxygen to the encephalon. Preterm babies have trouble animate and getting oxygen into their claret, because their lungs are not fully developed. If a baby'southward brain does not get enough oxygen, the neurons in the brain cannot survive. Earlier a babe is built-in, the nutrition it receives from its mother is perfectly adjusted for the baby's specific needs during each timepoint in evolution. For instance, during the third trimester, oligodendrocytes need certain kinds of fats to make myelin. If a baby is born before the 3rd trimester ends, the baby could develop brain injury if it doesn't have the right nutrients to make myelin. Doctors who take intendance of preterm babies piece of work to provide the diet that the baby would be receiving if they had not been born early, to help with good for you brain development.
Conclusion
Together, all the changes that a baby experiences when they are built-in early on can touch how the babe'southward encephalon develops. If the encephalon is non able to develop normally, the baby may abound up to accept problem in schoolhouse or may accept serious health problems. Although scientists and doctors are working on figuring out the best way to accept care of preterm babies, at that place is withal a lot work to be done. It is essential to continue researching how a baby's brain develops and what happens when encephalon development is interrupted when a babe is born early, so that we can find different ways to minimize the brain injury that these babies can have.
Glossary
Trimester: ↑ Pregnancy is divided into iii stages. Each of these stages is called a trimester.
Preterm Baby: ↑ A normal baby is built-in between 37 and xl weeks of evolution. If a baby is born early, earlier 37 weeks, and then doctors phone call the baby "preterm."
Synapse: ↑ The place where messages are sent from one neuron to another neuron across a tiny infinite.
Term Baby: ↑ A baby who is built-in on time, at 37–40 weeks of development.
Inflammation: ↑ When the body detects an injury or infection, it makes a protective response to help itself heal. This inflammation response involves the release of certain molecules that can contribute to brain injury.
Conflict of Involvement Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed every bit a potential conflict of interest.
References
[one] ↑ Blencowe, H., Cousens, Due south., Oestergaard, M. Z., Chou, D., Moller, A. B., Narwal, R., et al. 2012. National, regional, and worldwide estimates of preterm birth rates in the yr 2010 with fourth dimension trends since 1990 for selected countries: a systematic analysis and implications. Lancet 379(9832):2162–72. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)60820-4
[2] ↑ Bouyssi-Kobar, Grand., du Plessis, A. J., McCarter, R., Brossard-Racine, M., Murnick, J., Tinkleman, L., et al. 2016. Third Trimester Encephalon Growth in preterm infants compared with in utero healthy fetuses. Pediatrics 138(5):e20161640. doi: 10.1542/peds.2016-1640
[3] ↑ Volpe, J. J. 2003. Cerebral white thing injury of the premature infant-more common than you think. Pediatrics 112(1):176–lxxx. doi: 10.1542/peds.112.ane.176
[four] ↑ Men, W., Falk, D., Sun, T., Chen, Westward., Li, J., Yin, D., et al. 2014. The corpus callosum of Albert Einstein's brain: another clue to his high intelligence? Brain 137(4):1–viii. doi: 10.1093/brain/awt252
[v] ↑ Fischi-Gómez, E., Vasung, 50., Meskaldji, D. E., Lazeyras, F., Borradori-Tolsa, C., and Hagmann, P. 2014. Structural brain connectivity in school-age preterm infants provides prove for impaired networks relevant for higher social club cognitive skills and social cognition. Cereb. Cortex 25(nine):2793–805. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhu073
Source: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/283211
0 Response to "What Brain Changes Are Consistent With Premature Babies"
Post a Comment